Is Java Pass by Reference or Pass by Value?
Java manipulates objects ‘by reference’, but it passes object references to methods ‘by value’.
Consider the following program:
public class MainJava
{
public static void main(String[] arg) {
Foo f = new Foo("f");
// It won't change the reference!
changeReference(f);
// It will modify the object that the reference variable "f" refers to!
modifyReference(f);
}
public static void changeReference(Foo a) {
Foo b = new Foo("b");
a = b;
}
public static void modifyReference(Foo c) {
c.setAttribute("c");
}
}
Recommended Article
I will explain this in steps:
- Declaring a reference named
fof typeFooand assign it to a new object of typeFoowith an attribute"f".
Foo f = new Foo("f");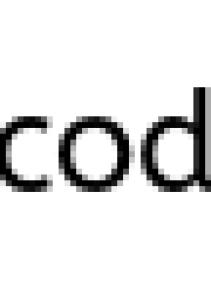
- From the method side, a reference of type
Foowith a nameais declared and it’s initially assigned tonull.
public static void changeReference(Foo a)
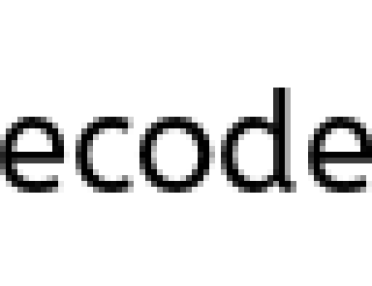
- As you call the method
changeReference, the referenceawill be assigned to the object which is passed as an argument.changeReference(f);
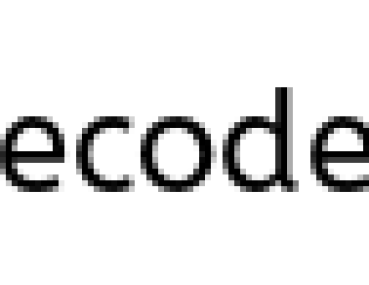
- Declaring a reference named
bof typeFooand assign it to a new object of typeFoowith an attribute"b".Foo b = new Foo("b");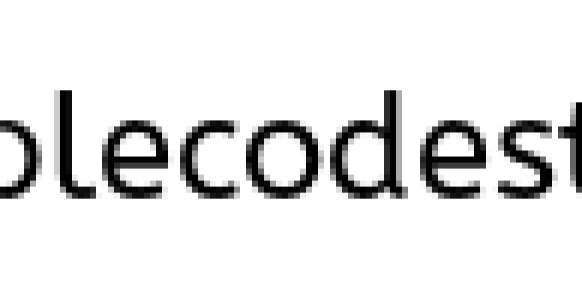
a = bis re-assigning the referenceaNOTfto the object whose its attribute is"b".
That is Only the references of a is modified, not the original ones(Reference offremains the same)
- As you call
modifyReference(Foo c)method, a referencecis created and assigned to the object with attribute"f".
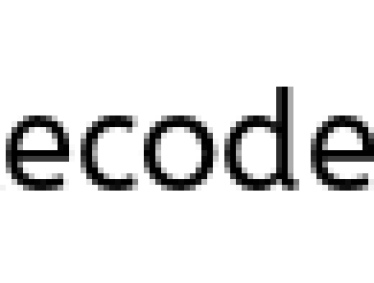
- c.setAttribute(“c”); will change the attribute of the object that reference
cpoints to it, and it’s same object that referencefpoints to it.
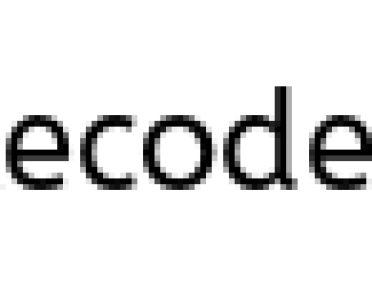
I hope you understand now how passing objects as arguments works in Java :)




