How To Create Table Layout in an Android Application
In this Tutorial, you will Learn How to create Relative Layout
Here you go!!!!
Before creating an android application using Eclipse, let us see some of the key terms involved while developing this application.
Key terms involved in this project:
Table Layout: The TableLayout groups views into rows and columns. You use the <TableRow> element to designate a row in the table. Each row can contain one or more views. Each view you place within a row forms a cell. The width for each column is determined by the largest width of each cell in that column.
The tutorial is about how to display an activity in table layout.
This project is developed in Eclipse 4.2 (Juno) and tested with Android 2.2
If you are new to android application project, to create a new project in Eclipse refer Creation of Android Project.
Coding:
Now let’s go to the coding section. This project requires following files.
** UPDATE: Android Complete tutorial now available here.
Source Code:
- Tablelayout.java (Activity in tablelayout)
Activity Files:
- activity_tablelayout.xml - tablelayout activity
res – Values:
- strings.xml - strings available in table layout
Manifest file:
- AndroidManifest.xml
Here is the coding for the above files.
Tabletlayout.java:
package com.example.tablelayout; //Package tablelayout
import android.os.Bundle; // A mapping from String values to various Parcelable types.
import android.app.Activity; // Required to create an activity.
import android.view.Menu; // Interface for managing the items in a menu.
public class Tablelayout extends Activity { // all classes extends activity
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Create an activity/ screen
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// displays activity tablelayout in table layout when app starts
setContentView(R.layout.activity_tablelayout);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_tablelayout, menu);
return true;
}
}
activity_tablelayout.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/tableLayout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<!-- 2 columns -->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/Row1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="5dip" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text1"
android:text="Column1"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:text="Column2" />
</TableRow>
<!-- edittext span 2 column -->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/Row2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="5dip" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/Textbox1"
android:layout_span="2"
android:text="Column1 and 2" />
</TableRow>
<!-- just draw a line -->
<View
android:layout_height="2dip"
android:background="#00FFFF" />
<!-- 3 columns -->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/Row3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="5dip" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text2"
android:text="Column1"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:text="Column2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:text="Column3" />
</TableRow>
<!-- display this button in 3rd column via layout_column(zero based) -->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/Row4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="5dip" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_column="2"
android:text="Column3" />
</TableRow>
<!-- display this button in 2nd column via layout_column(zero based) -->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/Row5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="5dip" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="Column2" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
Run the android application:
Android applications can be run on the android devices. You can either connect hardware to the system to test the application or you can use the android virtual devices (AVD) Manager to create/manage the virtual devices running on emulator to run the application.
If you are new to create a Android Virtual Device (AVD), refer Creating Android Virtual Device.
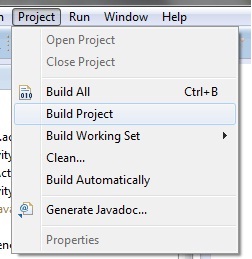
To run the application/ project, Build your project using Project -> Build Project.
This will show errors in Console window at the bottom of the working area in case your project contains.
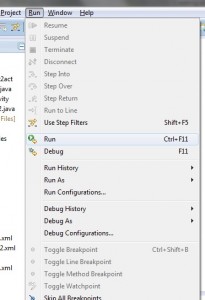
If your build is successful, Run your application using Run -> Run or Press Ctrl +F11.
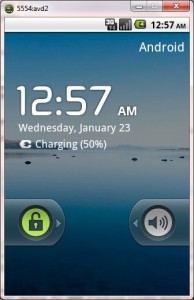
Upon running the application, the emulator will be launched which displays the AVD on your screen.
You can see your app with the image set during the android project creation in AVD. Upon running the application, the emulator will be launched with the selected/ available AVD created on your screen.
To test your application, unlock the screen and double click on your app.
Table layout
Thus the android application project is executed successfully.
Click Here To Share This..!!
Share